

It also allows control and management of PCs and Servers on the network via Group Policy (so for example you could set all users’ home page on their browser to be your intranet, or you can prevent users from installing other software etc). For example, it knows that John Smith is in the Sales Group and is not allowed to access the HR folder on the file server. Once signed in, AD also governs what the users are, and are not, allowed to do or access (authorisation). So basically AD has a record of all your users, PCs and Servers and authenticates the users signing in ( the network logon ). Group Policy – for fine grained control and management of PCs and Servers on the domain.LDAP, NTLM, Kerberos (secure authentication between domain joined devices).
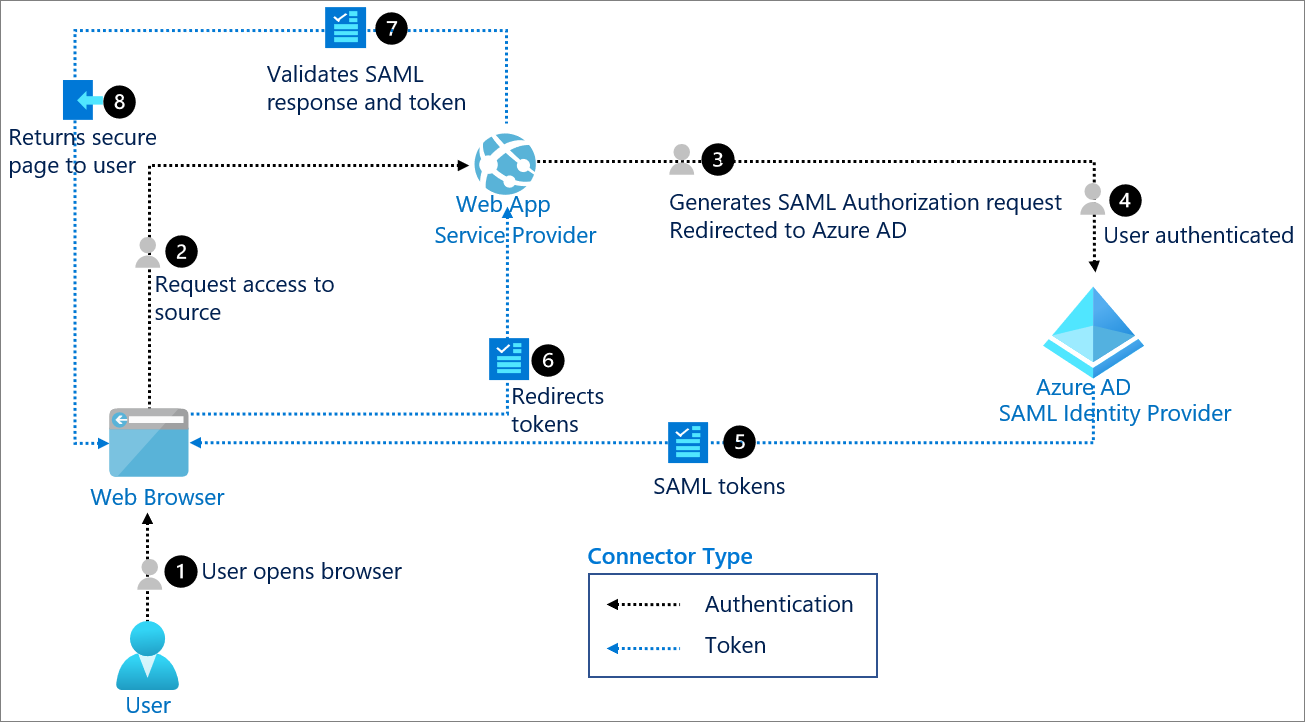
Common Authentication and Authorization provider.

In this guide, we’ll be exploring the key differences between Active Directory (AD), Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) and their relevance to you.ĪD stands for Active Directory. AD vs Azure AD – confused about the difference? We get it – the distinction isn’t immediately clear.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
